Durable Scaffolding Steel Struts – Adjustable And Versatile
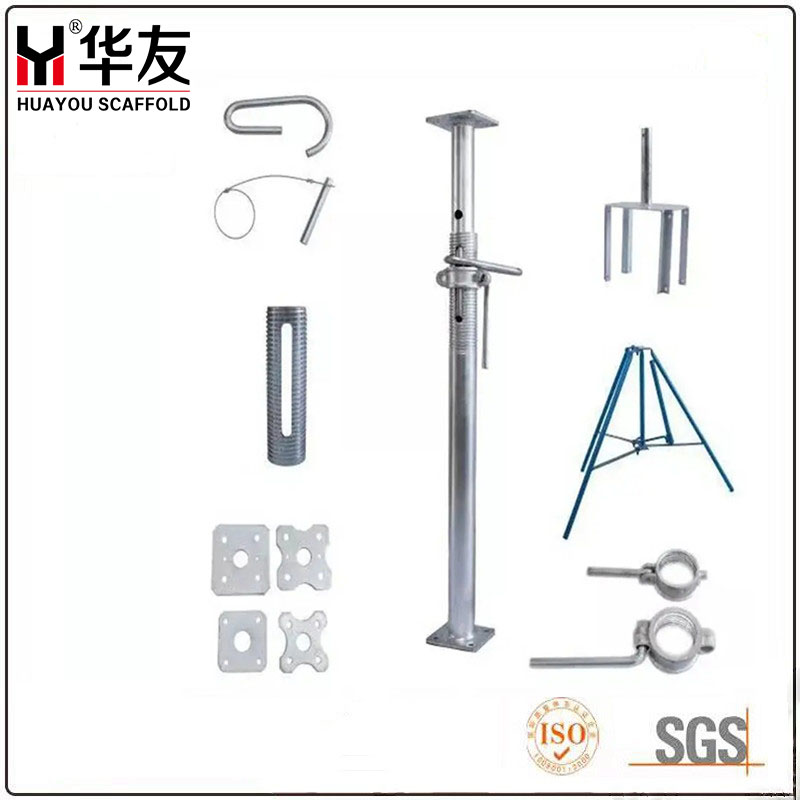
Scaffolding steel pillars are mainly used for formwork, beams and some other plywood to support concrete structures. Several years ago, all construction contractors used wooden poles that were prone to breakage and decay when pouring concrete. That is to say, steel pillars are safer, have a stronger load-bearing capacity, are more durable, and can also be adjusted to different lengths according to different heights.
Scaffolding Steel Prop have many different names, such as scaffolding pillars, supports, telescopic pillars, adjustable steel pillars, jacks, etc
Specification Details
|
Item |
Min Length-Max. Length |
Inner Tube(mm) |
Outer Tube(mm) |
Thickness(mm) |
|
Light Duty Prop |
1.7-3.0m |
40/48 |
48/56 |
1.3-1.8 |
|
1.8-3.2m |
40/48 |
48/56 |
1.3-1.8 |
|
|
2.0-3.5m |
40/48 |
48/56 |
1.3-1.8 |
|
|
2.2-4.0m |
40/48 |
48/56 |
1.3-1.8 |
|
| Heavy Duty Prop |
1.7-3.0m |
48/60 |
60/76 |
1.8-4.75 |
| 1.8-3.2m | 48/60 | 60/76 | 1.8-4.75 | |
| 2.0-3.5m | 48/60 | 60/76 | 1.8-4.75 | |
| 2.2-4.0m | 48/60 | 60/76 | 1.8-4.75 | |
| 3.0-5.0m | 48/60 | 60/76 | 1.8-4.75 |
Other Information
| Name | Base Plate | Nut | Pin | Surface Treatment |
| Light Duty Prop | Flower type/
Square type |
Cup nut | 12mm G pin/
Line Pin |
Pre-Galv./
Painted/ Powder Coated |
| Heavy Duty Prop | Flower type/
Square type |
Casting/
Drop forged nut |
16mm/18mm G pin | Painted/
Powder Coated/ Hot Dip Galv. |
Specification Details
1. Outstanding load-bearing capacity and safety
High-strength materials: Made of high-quality steel, especially for heavy-duty pillars, larger pipe diameters (such as OD60mm, OD76mm, OD89mm) and thicker wall thicknesses (≥2.0mm) are used, along with heavy-duty nuts formed by casting or forging, ensuring a solid and stable structure.
Far superior to wooden supports: Compared with traditional wooden poles that are prone to breakage and decay, steel pillars have extremely high compressive strength and can safely and reliably support concrete formwork, beams and other structures, greatly reducing safety risks during construction.
2. Flexible and adjustable, with wide applicability
Adjustable height: With an inner and outer tube telescopic design and in combination with adjusting nuts (such as cup-shaped nuts for light pillars), the length of the pillar can be easily and precisely adjusted to quickly adapt to different construction height requirements, enhancing the flexibility and efficiency of construction.
3. Strong durability and long service life
Corrosion-resistant treatment: Multiple surface treatment options are provided, such as painting, pre-galvanizing and electro-galvanizing, effectively preventing rust and extending the product's service life in harsh construction site environments.
Reusable: The sturdy steel structure makes it less prone to damage and allows for multiple cycles in different projects, offering high overall cost-effectiveness.
4. Product series, diverse choices
Both lightweight and heavy-duty: The product line covers both lightweight and heavy-duty types, meeting the needs of various construction scenarios from low load to high load. Users can choose the most suitable and economical product according to their specific load-bearing requirements.
5. Standardization and convenience
As a mature industrial product, it has uniform specifications, is easy to install and disassemble, and is conducive to on-site management and rapid construction.


FAQS
1. What are the main differences between light pillars and heavy pillars?
The main differences lie in three aspects:
Pipe size and thickness: Light pillars use smaller-sized pipes (such as OD40/48mm), while heavy pillars use larger and thicker pipes (such as OD60/76mm, with a thickness usually ≥2.0mm).
Nut type: Cup nuts are used for light pillars, while stronger cast or drop forged nuts are used for heavy pillars.
Weight and load-bearing capacity: Light pillars are lighter in weight, while heavy pillars are heavier and have a stronger load-bearing capacity.
2. Why are steel pillars better than traditional wooden pillars?
Steel pillars have significant advantages over wooden pillars
Higher safety: Less prone to breakage and stronger load-bearing capacity.
More durable: Anti-corrosion treatments (such as painting and galvanizing) make it less prone to decay and have a longer service life.
Adjustable: The height can be flexibly adjusted according to the construction needs.
3. What are the common surface treatment methods for steel pillars? What is its function?
Common surface treatment methods include painting, pre-galvanizing and electro-galvanizing. The main function of these treatments is to prevent steel from rusting and corroding, thereby extending the service life of the pillars in outdoor or damp construction environments.
4. What are the main uses of steel pillars in construction?
Steel pillars are mainly used to support concrete structures. When pouring concrete, it is used in conjunction with formwork, beams and plywood to provide stable temporary support for concrete components (such as floor slabs, beams and columns) until the concrete reaches sufficient strength.
5. What are the common alternative names or names for steel pillars?
Steel pillars have various names in different regions and application scenarios. Common ones include: scaffolding pillars, supports, telescopic pillars, adjustable steel pillars, jacks, etc. These names all reflect its core functions of adjustable height and supporting role.